Kotlin Notebook 支持的输出格式
Kotlin Notebook 支持多种输出类型,包括文本、HTML 和图片。借助外部库,您可以扩展输出选项,并通过图表、电子表格等方式可视化数据。
每个输出都是一个 JSON 对象,将 Jupiter MIME type 映射到一些数据。Kotlin Notebook 会从此映射中选择支持的、优先级最高的 MIME type,并按如下方式进行渲染:
- 文本使用
text/plainMIME type。 - BufferedImage 类使用
image/pngMIME type,该类型映射到 Base64 字符串。 - Image 类以及 LaTeX 格式使用
text/htmlMIME type,其中包含img标签。 - Kotlin DataFrame 表格和 Kandy 图使用它们自己的内部 MIME type,这些类型由静态 HTML 或图片支持。这样,您就可以在 GitHub 上显示它们。
您可以手动设置映射,例如,使用 Markdown 作为单元格输出:
MimeTypedResult(
mapOf(
"text/plain" to "123",
"text/markdown" to "# HEADER",
//other mime:value pairs
)
)要显示任何类型的输出,请使用 DISPLAY() 函数。它还可以组合多个输出:
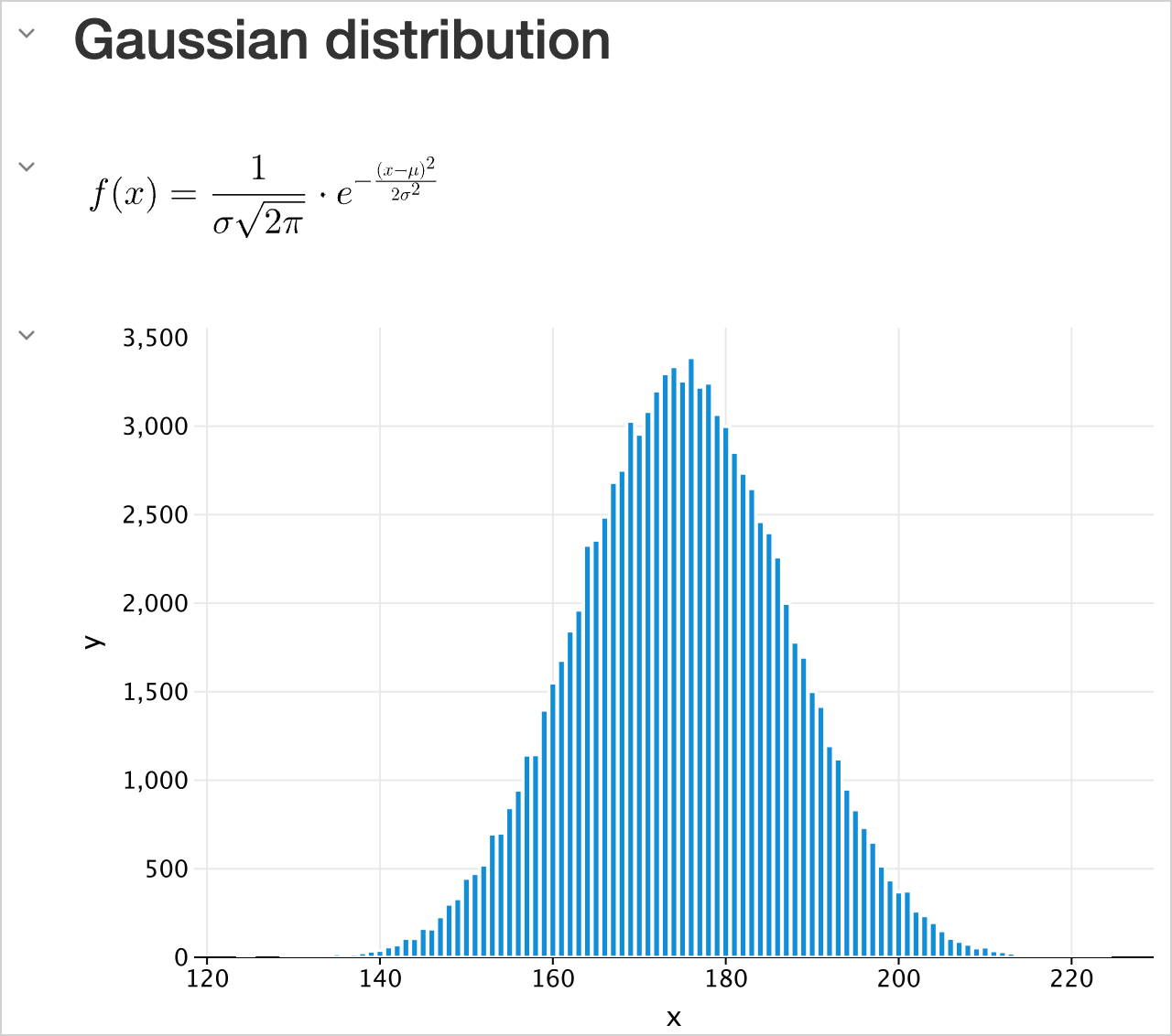
DISPLAY(HTML("<h2>Gaussian distribution</h2>"))
DISPLAY(LATEX("f(x) = \\frac{1}{\\sigma \\sqrt{2\\pi}} \\cdot e^{-\\frac{(x - \\mu)^2}{2\\sigma^2}}"))
val experimentX = experimentData.map { it.key }
val experimentY = experimentData.map { it.value }
DISPLAY(plot {
bars {
x(experimentX)
y(experimentY)
}
})
文本
纯文本
最简单的输出类型是纯文本。它用于打印语句、变量值或代码中的任何基于文本的输出:
val a1: Int = 1
val a2: Int = 2
var a3: Int? = a1 + a2
"My answer is $a3"
- 如果单元格的结果无法渲染并显示为任何输出类型,它将使用
toString()函数以纯文本形式打印。 - 如果您的代码包含错误,Kotlin Notebook 会显示错误消息和堆栈跟踪,为调试提供见解。
富文本
选择 Markdown 类型的单元格以使用富文本。这样,您可以使用 Markdown 和 HTML 标记来格式化内容,包括列表、表格、字体样式、代码块等。HTML 可以包含 CSS 样式和 JavaScript。
## Line magics
| Spell | Description | Example |
|------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| <code>%use</code> | 为支持的库注入代码:artifact 解析、默认导入、初始化代码、类型渲染器。 | <code>%use klaxon(5.5), lets-plot</code> |
| <code>%trackClasspath</code> | 记录当前 classpath 的任何更改。有助于调试 artifact 解析失败。 | <code>%trackClasspath [on |off]</code> |
| <code>%trackExecution</code> | 记录将要执行的代码片段。有助于调试库支持。 | <code>%trackExecution [all|generated|off]</code> |
| <code>%useLatestDescriptors</code> | 使用可用的最新版本库描述符。默认情况下,使用捆绑的描述符。 | <code>%useLatestDescriptors [on|off]</code> |
| <code>%output</code> | 输出捕获设置。 | <code>%output --max-cell-size=1000 --no-stdout --max-time=100 --max-buffer=400</code> |
| <code>%logLevel</code> | 设置日志级别。 | <code>%logLevel [off|error|warn|info|debug]</code> |
<ul><li><a href="https://github.com/Kotlin/kotlin-jupyter/blob/master/docs/magics.md">关于行魔术命令的更多详细信息</a>。</li>
<li><a href="https://github.com/Kotlin/kotlin-jupyter/blob/master/docs/magics.md">查看支持库的完整列表</a>。</li></ul>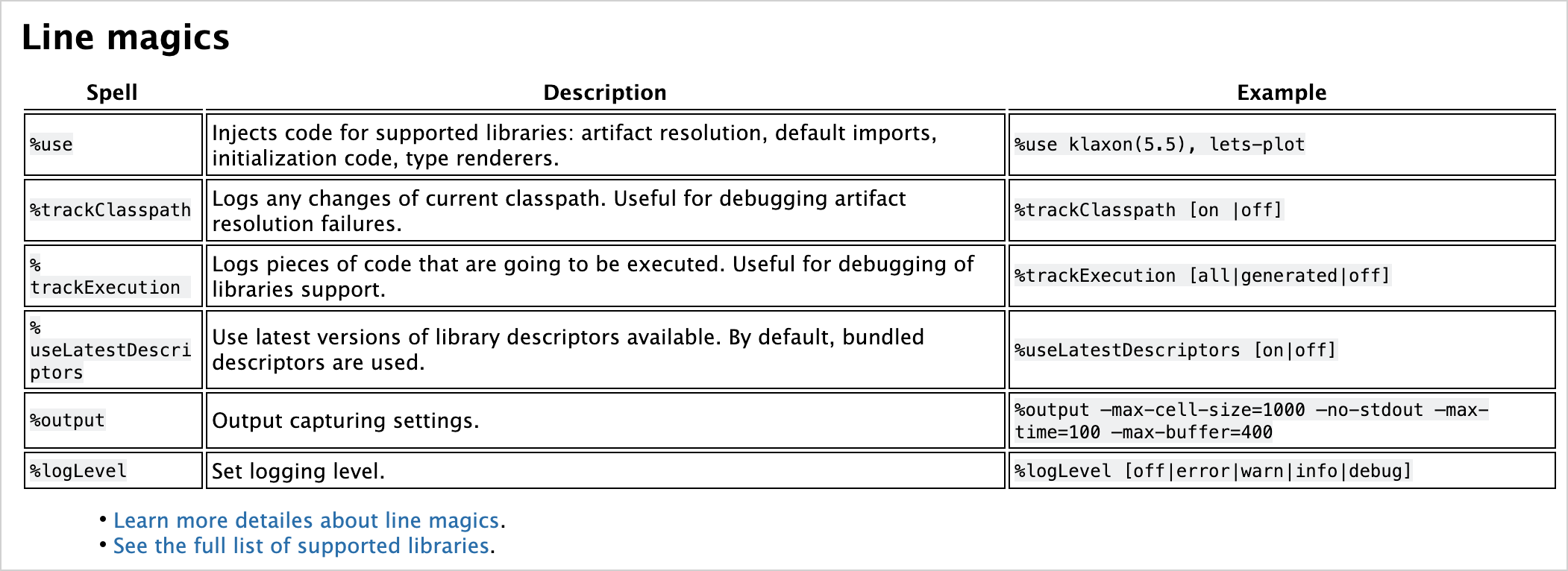
HTML
Kotlin Notebook 可以直接渲染 HTML,执行脚本甚至嵌入网站:
HTML("""
<p>Counter: <span id="ctr">0</span> <button onclick="inc()">Increment</button></p>
<script>
function inc() {
let counter = document.getElementById("ctr")
counter.innerHTML = parseInt(counter.innerHTML) + 1;
}
</script>
""")
在文件顶部将您的 Notebook 标记为 Trusted(信任)以执行脚本。
图片
借助 Kotlin Notebook,您可以显示来自文件、生成的图表或任何其他视觉媒体的图片。静态图片可以以 .png、jpeg 和 .svg 等格式显示。
缓冲图片
默认情况下,您可以使用 BufferedImage 类来显示图片:
import java.awt.Color
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage
val width = 300
val height = width
val image = BufferedImage(width, height, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_ARGB)
val graphics = image.createGraphics()
graphics.background = Color.BLACK
graphics.clearRect(0, 0, width, height)
graphics.setRenderingHint(
java.awt.RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING,
java.awt.RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON
)
graphics.color = Color.WHITE
graphics.fillRect(width / 10, height * 8 / 10, width * 10 / 20, height / 10)
graphics.dispose()
加载的图片
借助 lib-ext 库,您可以扩展标准的 Jupyter 功能并显示从网络加载的图片:
%use lib-ext(0.11.0-398)Image("https://kotlinlang.org/docs/images/kotlin-logo.png", embed = false).withWidth(300)
嵌入图片
从网络加载图片的缺点是如果链接失效或您失去网络连接,图片就会消失。为了解决这个问题,请使用嵌入图片,例如:
val kotlinMascot = Image("https://blog.jetbrains.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/DSGN-16174-Blog-post-banner-and-promo-materials-for-post-about-Kotlin-mascot_3.png", embed = true).withWidth(400)
kotlinMascot
数学公式和方程式
您可以使用 LaTeX 格式渲染数学公式和方程式,这是一种广泛用于学术界的排版系统:
将扩展 Jupyter 内核功能的
lib-ext库添加到您的 Notebook:none%use lib-ext(0.11.0-398)在新单元格中运行您的公式:
noneLATEX("c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2 a b \\cos\\alpha")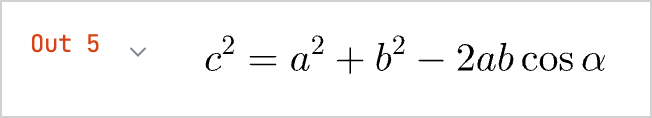
数据帧
借助 Kotlin Notebook,您可以使用数据帧可视化结构化数据:
将 Kotlin DataFrame 库添加到您的 Notebook:
none%use dataframe创建数据帧并在新单元格中运行:
kotlinval months = listOf( "January", "February", "March", "April", "May", "June", "July", "August", "September", "October", "November", "December" ) // Sales data for different products and months: val salesLaptop = listOf(120, 130, 150, 180, 200, 220, 240, 230, 210, 190, 160, 140) val salesSmartphone = listOf(90, 100, 110, 130, 150, 170, 190, 180, 160, 140, 120, 100) val salesTablet = listOf(60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110, 120, 110, 100, 90, 80, 70) // A data frame with columns for Month, Sales, and Product val dfSales = dataFrameOf( "Month" to months + months + months, "Sales" to salesLaptop + salesSmartphone + salesTablet, "Product" to List(12) { "Laptop" } + List(12) { "Smartphone" } + List(12) { "Tablet" }, )该数据帧使用
dataFrameOf()函数,并包含 12 个月内售出的产品数量(笔记本电脑、智能手机和平板电脑)。探索数据帧中的数据,例如,查找销售额最高的产品和月份:
nonedfSales.maxBy("Sales")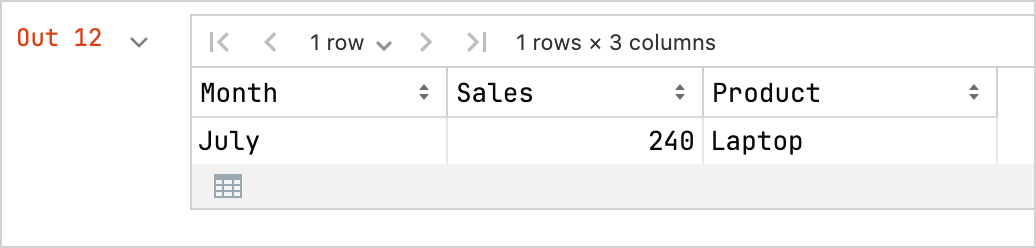
您还可以将数据帧导出为 CSV 文件:
kotlin// Export your data to CSV format dfSales.writeCSV("sales-stats.csv")
图表
您可以在 Kotlin Notebook 中直接创建各种图表来可视化数据:
将 Kandy 绘图库添加到您的 Notebook:
none%use kandy使用相同的数据帧并在新单元格中运行
plot()函数:kotlinval salesPlot = dfSales.groupBy { Product }.plot { bars { // Access the data frame's columns used for the X and Y axes x(Month) y(Sales) // Access the data frame's column used for categories and sets colors for these categories fillColor(Product) { scale = categorical( "Laptop" to Color.PURPLE, "Smartphone" to Color.ORANGE, "Tablet" to Color.GREEN ) legend.name = "Product types" } } // Customize the chart's appearance layout.size = 1000 to 450 layout.title = "Yearly Gadget Sales Results" } salesPlot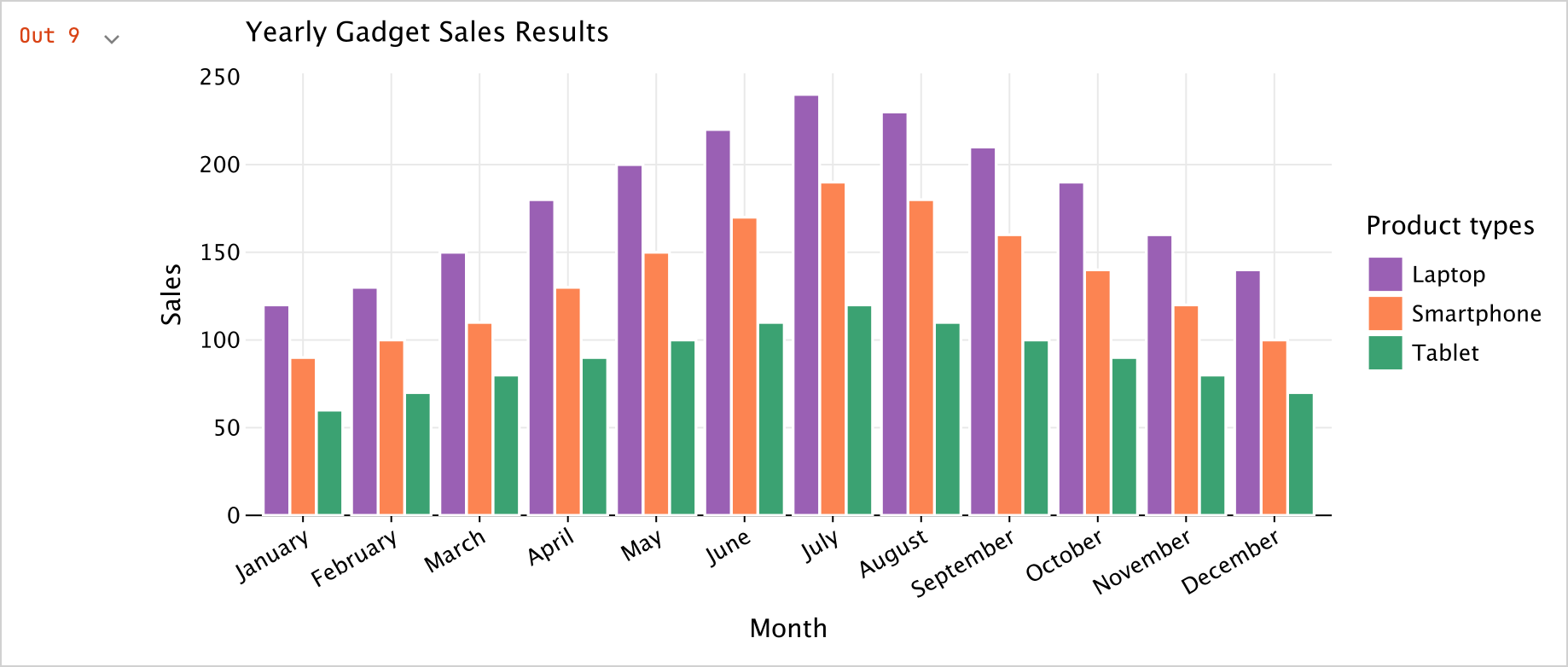
您还可以以
.png、jpeg、.html或.svg格式导出您的绘图:kotlin// Specify the output format for the plot file: salesPlot.save("sales-chart.svg")
