使用 Lets-Plot for Kotlin 进行数据可视化
Lets-Plot for Kotlin (LPK) 是一个多平台绘图库,它将 R 语言的 ggplot2 库 移植到 Kotlin。LPK 将功能丰富的 ggplot2 API 带入 Kotlin 生态系统,使其适用于需要复杂数据可视化能力的科学家和统计学家。
LPK 面向多种平台,包括 Kotlin notebook、Kotlin/JS、JVM 的 Swing、JavaFX 和 Compose Multiplatform。此外,LPK 与 IntelliJ、DataGrip、DataSpell 和 PyCharm 无缝集成。
本教程演示了如何在 IntelliJ IDEA 中使用 Kotlin Notebook,借助 LPK 和 Kotlin DataFrame 库创建不同绘图类型。
开始之前
Kotlin Notebook 依赖于 Kotlin Notebook 插件,该插件默认捆绑并启用在 IntelliJ IDEA 中。
如果 Kotlin Notebook 特性不可用,请确保该插件已启用。关于更多信息,请参见 设置环境。
创建一个新的 Kotlin Notebook 来使用 Lets-Plot:
选择 文件 | 新建 | Kotlin Notebook。
在你的 Notebook 中,运行以下命令导入 LPK 和 Kotlin DataFrame 库:
kotlin%use lets-plot %use dataframe
准备数据
让我们创建一个 DataFrame,用于存储柏林、马德里和加拉加斯这三个城市的月平均气温模拟数据。
使用 Kotlin DataFrame 库的 dataFrameOf() 函数生成 DataFrame。将以下代码片段粘贴到你的 Kotlin Notebook 并运行:
// months 变量存储了一年中的 12 个月份
val months = listOf(
"January", "February",
"March", "April", "May",
"June", "July", "August",
"September", "October", "November",
"December"
)
// tempBerlin, tempMadrid 和 tempCaracas 变量存储了每个月的温度值
val tempBerlin =
listOf(-0.5, 0.0, 4.8, 9.0, 14.3, 17.5, 19.2, 18.9, 14.5, 9.7, 4.7, 1.0)
val tempMadrid =
listOf(6.3, 7.9, 11.2, 12.9, 16.7, 21.1, 24.7, 24.2, 20.3, 15.4, 9.9, 6.6)
val tempCaracas =
listOf(27.5, 28.9, 29.6, 30.9, 31.7, 35.1, 33.8, 32.2, 31.3, 29.4, 28.9, 27.6)
// df 变量存储了一个包含月度记录、温度和城市三列的 DataFrame
val df = dataFrameOf(
"Month" to months + months + months,
"Temperature" to tempBerlin + tempMadrid + tempCaracas,
"City" to List(12) { "Berlin" } + List(12) { "Madrid" } + List(12) { "Caracas" }
)
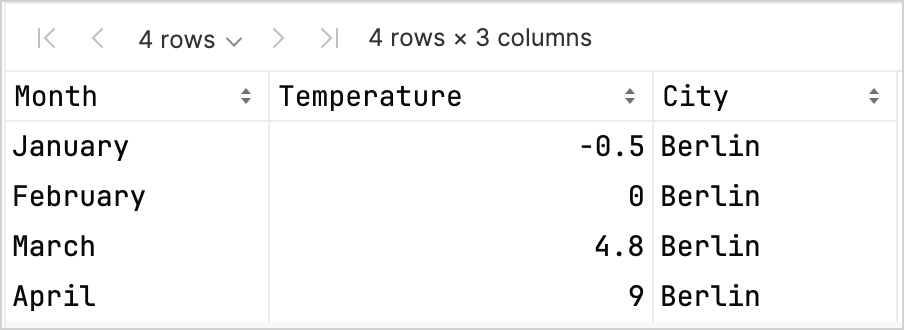
df.head(4)你可以看到 DataFrame 有三列:Month、Temperature 和 City。DataFrame 的前四行包含柏林从一月到四月的温度记录:
要使用 LPK 库创建绘图,你需要将数据 (df) 转换为以键值对形式存储数据的 Map 类型。你可以使用 .toMap() 函数轻松地将 DataFrame 转换为 Map:
val data = df.toMap()创建散点图
让我们在 Kotlin Notebook 中使用 LPK 库创建一个散点图。
一旦你的数据是 Map 格式,就可以使用 LPK 库的 geomPoint() 函数生成散点图。你可以指定 X 轴和 Y 轴的值,并定义类别及其颜色。此外,你可以 自定义 绘图的大小和点形状,以满足你的需求:
// 指定 X 轴和 Y 轴、类别及其颜色、绘图大小和绘图类型
val scatterPlot =
letsPlot(data) { x = "Month"; y = "Temperature"; color = "City" } + ggsize(600, 500) + geomPoint(shape = 15)
scatterPlot结果如下:
创建箱线图
让我们在箱线图中可视化 数据。使用 LPK 库的 geomBoxplot() 函数生成绘图,并使用 scaleFillManual() 函数 自定义 颜色:
// 指定 X 轴和 Y 轴、类别、绘图大小和绘图类型
val boxPlot = ggplot(data) { x = "City"; y = "Temperature" } + ggsize(700, 500) + geomBoxplot { fill = "City" } +
// 自定义颜色
scaleFillManual(values = listOf("light_yellow", "light_magenta", "light_green"))
boxPlot结果如下:
创建二维密度图
现在,让我们创建一个二维密度图来可视化某些随机数据的分布和集中。
准备二维密度图的数据
导入依赖项以处理数据并生成绘图:
kotlin%use lets-plot @file:DependsOn("org.apache.commons:commons-math3:3.6.1") import org.apache.commons.math3.distribution.MultivariateNormalDistribution关于导入依赖项到 Kotlin Notebook 的更多信息,请参见 Kotlin Notebook 文档。
将以下代码片段粘贴到你的 Kotlin Notebook 并运行,以创建二维数据点集:
kotlin// 为三种分布定义协方差矩阵 val cov0: Array<DoubleArray> = arrayOf( doubleArrayOf(1.0, -.8), doubleArrayOf(-.8, 1.0) ) val cov1: Array<DoubleArray> = arrayOf( doubleArrayOf(1.0, .8), doubleArrayOf(.8, 1.0) ) val cov2: Array<DoubleArray> = arrayOf( doubleArrayOf(10.0, .1), doubleArrayOf(.1, .1) ) // 定义样本数量 val n = 400 // 为三种分布定义均值 val means0: DoubleArray = doubleArrayOf(-2.0, 0.0) val means1: DoubleArray = doubleArrayOf(2.0, 0.0) val means2: DoubleArray = doubleArrayOf(0.0, 1.0) // 从三种多元正态分布生成随机样本 val xy0 = MultivariateNormalDistribution(means0, cov0).sample(n) val xy1 = MultivariateNormalDistribution(means1, cov1).sample(n) val xy2 = MultivariateNormalDistribution(means2, cov2).sample(n)从上面的代码中,
xy0、xy1和xy2变量存储了包含二维 (x, y) 数据点的数组。将你的数据转换为
Map类型:kotlinval data = mapOf( "x" to (xy0.map { it[0] } + xy1.map { it[0] } + xy2.map { it[0] }).toList(), "y" to (xy0.map { it[1] } + xy1.map { it[1] } + xy2.map { it[1] }).toList() )
生成二维密度图
使用上一步骤中的 Map,创建一个二维密度图 (geomDensity2D),并以散点图 (geomPoint) 作为背景,以便更好地可视化数据点和异常值。你可以使用 scaleColorGradient() 函数自定义颜色刻度:
val densityPlot = letsPlot(data) { x = "x"; y = "y" } + ggsize(600, 300) + geomPoint(
color = "black",
alpha = .1
) + geomDensity2D { color = "..level.." } +
scaleColorGradient(low = "dark_green", high = "yellow", guide = guideColorbar(barHeight = 10, barWidth = 300)) +
theme().legendPositionBottom()
densityPlot结果如下:
接下来
- 在 Lets-Plot for Kotlin 文档 中探索更多绘图示例。
- 查阅 Lets-Plot for Kotlin 的 API 参考。
- 在 Kotlin DataFrame 和 Kandy 库文档中了解如何使用 Kotlin 转换和可视化数据。
- 查找关于 Kotlin Notebook 用法和关键特性 的更多信息。
